
Can Facial Recognition Be Trusted for Immigration Control?
Not so long ago, we were able to come across facial recognition technologies in movies only. The plots of numerous detective series and action films have been built around the story about a detective who has managed to establish connection between seemingly unrelated incidents using facial recognition technology.
In movie theaters or on our home TV screens, we could see how an investigator analyzed the footage from the street cameras and how facial recognition software identified a possible suspect who crossed the border using counterfeit documents.
Today, this technology has made its way from TV screens into our daily life. While traditional methods like passport checks and biometric scans have long served their purpose, advancements in technology have introduced facial recognition as a game-changer.
In an increasingly digitalized world, reliable identity verification is paramount. This is why facial recognition technology has become a hot topic in immigration and law enforcement. As the world becomes more connected, the use of facial recognition in immigration procedures has become increasingly common. From border control to passport processing, this technology is changing the way we approach and manage immigration.
In this blog post, we will explore how facial recognition is used in immigration, the potential benefits and drawbacks, and the ethical considerations surrounding its implementation.
How is Facial Recognition Used in Immigration Control?
At present, immigration procedures heavily rely on facial recognition technologies. They are extensively utilized to confirm traveler IDs and strengthen security protocols at airports and border control checkpoints worldwide.
Here are real life examples of using facial recognition technologies in immigration control:
Facial Recognition Entry/Exit System (US). Implemented at select airports and land borders, FREES uses facial recognition technology to compare the face of an individual presenting a passport to a traveler database. This allows for faster processing times and enhanced security by identifying potential threats.
ePassport Gates (UK). Automated border control gates that use facial recognition to match the face of the passport holder to the biometric data stored on the passport chip. This streamlines the border crossing process for frequent travelers.
Passportless Travel (UK). A trial program that allows US passport holders to enter the UK without a physical passport.
eGate Program (Canada). Automated border control kiosks that combine facial recognition and iris scanning to verify the identity of travelers. This technology is used at major international airports.
Mobile Entry Program (Canada). A mobile application that allows Canadian citizens and permanent residents to use their smartphone for facial recognition authentication at designated border crossings.
Mobile Passport (Australia). A mobile application that allows Australian citizens to submit their passport and biometric information for remote verification before arriving at the border. This streamlines the border crossing process by allowing travelers to clear customs and immigration without having to present their physical passport.
To better understand how facial recognition technologies in immigration control work, let’s have a look at the case of JFK Airport where security control was revolutionized by facial recognition technologies.
Case
In the bustling metropolis of New York City, John F. Kennedy International Airport (JFK) serves as a major gateway for international travelers. To enhance security and streamline immigration processing, JFK has used the transformative power of facial recognition.
Challenge
The airport faced significant challenges in managing the influx of millions of passengers annually. Traditional methods of identity verification, such as passport checks and manual biometric scans, were time-consuming and prone to human error. This resulted in long queues and delays that both frustrated travelers and posed security risks.
Solution
In partnership with US Customs and Border Protection (CBP), JFK implemented facial recognition technology at its international terminals. The system consisted of advanced cameras and algorithms capable of capturing and analyzing facial images in real-time.
Implementation
Passengers enrolled in CBP’s Global Entry program were given the option to use facial recognition for expedited immigration processing. Upon arrival at JFK, they simply looked into a camera at kiosks designated for Global Entry members. The facial recognition technology scanned their faces and compared them against the biometric data stored in the CBP database. If a match was confirmed, the system processed their immigration documents, allowing them to enter the country.
Results
The implementation of facial recognition at JFK has yielded impressive results:
Reduced processing times. Average processing times for Global Entry members dropped from 7-8 minutes to less than 1 minute using facial recognition.
Improved security. The system’s accuracy and reliability have significantly reduced the risk of identity fraud and imposter threats.
Enhanced traveler experience. Passengers appreciate the speed and convenience of facial recognition, which eliminates long queues.
Facial recognition technology has proven to be a game-changer in immigration control at JFK Airport. By automating the identity verification process and improving efficiency, it has not only enhanced security but also transformed the traveler experience. As airports around the world seek to modernize their operations, the success of JFK serves as a model for the transformative potential of facial recognition in immigration control.
Most Common Applications of Facial Recognition in Immigration Control
In the era of globalization and increased cross-border movement, managing immigration effectively is crucial for maintaining national security and facilitating legitimate travel. The most common applications of facial recognition in immigration control are described below, covering such areas as border security and screening, automated passport control, identification of known travelers, and combating travel document fraud.
Border Security and Screening
Facial recognition technology has become an increasingly utilized tool in various aspects of border security and screening. This advanced technology allows authorities to quickly and accurately identify individuals entering or leaving a country, thus enhancing security measures and deterring potential threats.
One way facial recognition technology is utilized for border security is the use of surveillance cameras at border crossings. These cameras can scan the faces of individuals passing through and compare them to a database of known criminals or persons of interest.
In addition, some countries have also implemented biometric border control gates that use facial recognition technology to verify the identity of travelers. These advanced gates can quickly process passengers, speeding up the border control process and enhancing overall security.
Automated Passport Control
Another key application of facial recognition technology in border security is automated passport control. These systems use facial recognition algorithms to compare the traveler’s face with the photo on their passport, ensuring that the person presenting the document is indeed the rightful owner.
The procedure of automated passport control consists of two steps.
Identity verification. When travelers approach a passport control kiosk, the facial recognition technology captures an image of their face and compares it to the photo in their passport. This helps verify their identity without the need for human intervention.
Document authentication. In addition to comparing facial features, the technology also checks the security features of the passport, such as holograms and watermarks, to ensure that the document is genuine.
Facial recognition technology can help identify individuals who may be on a watchlist or have suspicious travel patterns, allowing border control agencies to take appropriate action to ensure the safety and security of their borders.
Identification of Known Travelers
Facial recognition technology has revolutionized the way we travel. Known travelers can now breeze through airports and other checkpoints by simply having their faces scanned. This technology has made the identification process quicker, more efficient, and more secure than ever before.
Known Traveler status refers to a category of trusted travelers who have been pre-screened and approved by government agencies of countries (like Canada or USA) participating in Global Entry and NEXUS programs to expedite their entry into a country. To qualify for Known Traveler status under programs like Global Entry or NEXUS, individuals must typically meet criteria such as: be a citizen or permanent resident of the participating countries, have a clean criminal record, be willing to undergo a background check and interview, and pay an application fee.
Known traveler programs, such as Global Entry and NEXUS, have integrated facial recognition technology into their systems. When enrolled participants enter a checkpoint, they can have their faces scanned instead of having to show physical identification or boarding passes. This not only saves time and eliminates the hassle of digging through bags for documents, but it also enhances security by verifying a person’s identity through unique facial features.
Combating Travel Document Fraud
Another important application of facial recognition technology in border security is combating travel document fraud.
Facial recognition systems use sophisticated algorithms to map an individual’s unique facial features. These features are then stored in a database and compared to real-time facial scans. When a travel document is presented, the system can quickly determine if the person holding it matches the biometrics on record.
Summing up, as technology continues to evolve, we can expect facial recognition to play an even greater role in ensuring the integrity of immigration control.
The Benefits of Facial Recognition Technology
Facial recognition technology has emerged as a powerful tool that unlocks a world of benefits for both security and efficiency. Here is how it is transforming the various aspects of our lives:
Enhanced Security and Efficiency
Facial recognition systems provide an unparalleled level of security. By analyzing unique facial features, they can accurately identify and verify individuals, even in crowded environments. This makes them ideal for applications such as airport security checks and financial transactions (banks and other financial institutions use facial recognition to authenticate customers, preventing fraud and identity theft).
Reduced Wait Times at Borders
Border crossings can be a tedious and time-consuming ordeal. However, facial recognition has revolutionized border management by speeding up passport control. Systems scan travelers’ faces and match them against government databases, significantly reducing waiting times for entry and departure.
Improved Detection of Imposters
Facial recognition technology is an effective deterrent against imposters and identity fraud. By comparing individuals’ faces to known databases, it can detect unauthorized access, prevent impersonation, and ensure the safety of sensitive areas.
Facial recognition technology holds immense promise for enhancing security, streamlining processes, and improving our daily lives. Its ability to accurately identify and verify individuals makes it an invaluable tool for law enforcement, border control, and a wide range of other applications.
Can Facial Recognition Be Trusted for Immigration Control?
While it offers potential benefits, the accuracy concerns, racial bias, and privacy issues raise serious doubts. Here are some significant concerns:
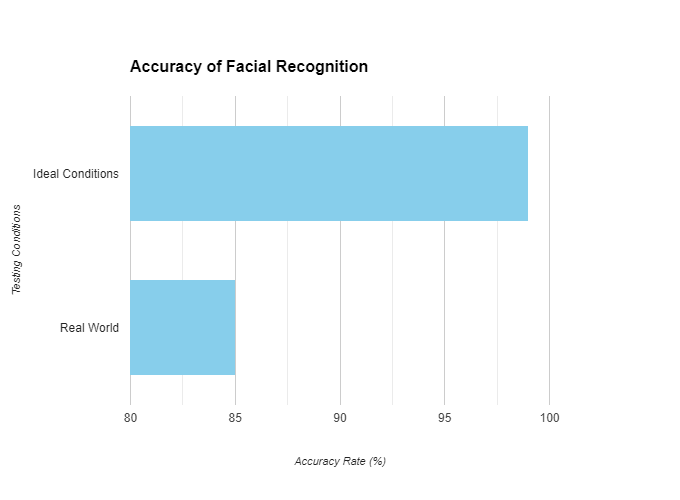
While companies claim high accuracy rates, real-world performance suffers due to lighting, facial expressions, and occlusion (hats, glasses). Error rates can range from 5% to 20%.
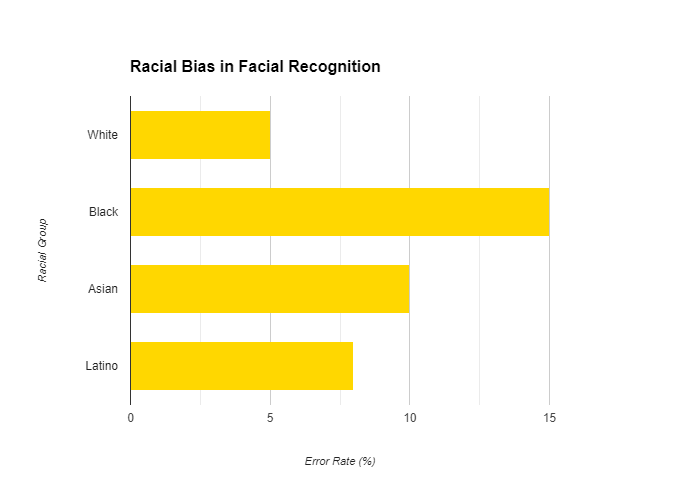
Studies, like A 2019 NIST study, show racial bias in some algorithms, leading to misidentification and unfair treatment, particularly for Black and Asian faces.
A 2021 IAPP survey found that 67% of people are concerned about government use of facial recognition technology.
So, the benefits are clear but can facial recognition be trusted? The answer is simple — not entirely.
Conclusion
In the evolving landscape of immigration, facial recognition technology offers both promise and challenges. While it has the potential to enhance security and streamline border crossing processes, its ethical and privacy implications must be carefully considered.
As we navigate the complexities of globalization and the need for secure borders, it is crucial to strike a balance between efficiency and human rights. By fostering transparent regulations, promoting responsible deployment, and respecting the privacy of individuals, we can harness the benefits of facial recognition technology while ensuring that it is employed ethically and responsibly.