
Police Facial Recognition: Safe or Scary? What You Need to Know (2024)
As we know, police forces around the world are increasingly adopting facial recognition technology for various purposes. Here are some real-world examples.
For example, New Zealand's police force is introducing an advanced facial recognition system, which represents a significant upgrade in their law enforcement technology. This "state of the art" system is expected to enhance their capabilities in identifying suspects, locating missing persons, and improving overall public safety. The introduction of this technology marks a major step forward in modernizing the country's policing efforts.
How is face recognition used by police? What are the benefits and concerts? We’ll explain everything in this blog post.
What is Face Recognition Technology?
Face recognition is a technology used to identify or confirm a person's identity based solely on their face. These systems can analyze photos, videos, or even live footage.
Many are familiar with face recognition through features like Apple's FaceID for unlocking phones. But that's just one example.
Beyond phone security, face recognition often works by comparing faces captured by special cameras to a database of individuals. These databases, also known as "watch lists," can include anyone, even those without criminal records. The images used for comparison can come from various sources, including social media.
Learn more about face recognition and use cases here: Face Recognition API
How is Face Recognition Used by Police?

Identifying Suspects
Police employ face recognition to match photographs or video footage from crime scenes to databases of known criminals in order to identify suspects. This can be especially beneficial in situations where usual identifying procedures are challenging.
Locating Missing Persons
Facial recognition can help locate lost children, adults, and other vulnerable people. By scanning public locations or social media, the technology can match faces to those in missing person databases.
Monitoring Public Spaces
Integrated with CCTV cameras, facial recognition technology can monitor public spaces for individuals on watch lists, such as suspected terrorists or wanted criminals, providing real-time alerts to law enforcement.
Plus, during large public events like concerts, sports games, or political rallies, facial recognition can scan crowds to detect known threats or persons of interest, enhancing security measures.
Border Security and Immigration Control
At border crossings and immigration checkpoints, facial recognition is used to confirm travelers' identities by comparing their faces to passport images or other official documents. This helps to prevent illegal entrance and identify people who use bogus documents. Learn more about using facial recognition for immigration control: Can Facial Recognition Be Trusted for Immigration Control?
Crime Prevention and Enhancing Evidence
By analyzing patterns and using facial recognition to identify repeat offenders or individuals involved in specific types of crimes, police can take preventive measures to reduce crime rates in certain areas.
Facial recognition technology can enhance the verification of evidence by identifying individuals captured in surveillance footage, thus bolstering court cases. Additionally, during ongoing investigations, facial recognition can generate new leads by identifying individuals appearing in multiple crime scene images or videos, linking them to various incidents. This ability to connect suspects to multiple crimes significantly aids law enforcement in building comprehensive cases and solving complex investigations.
Real Use Cases
Here are some real use cases that shows how the facial recognition technology helps police:
London Metropolitan Police Service. During trials, the Metropolitan Police reported that facial recognition technology helped in identifying suspects with a success rate of 70%, contributing to several arrests for serious offenses.
New York Police Department (NYPD). In 2018, the NYPD used facial recognition technology in over 2,800 cases, leading to approximately 1,000 arrests. This included identifications for serious crimes such as robbery, assault, and murder.
China. Chinese authorities have implemented facial recognition extensively. In 2018, facial recognition systems helped identify and apprehend more than 2,000 fugitives who attended public events, demonstrating the technology's effectiveness in large-scale surveillance.
Detroit Police Department. Since implementing facial recognition, the Detroit Police reported that the technology has assisted in identifying suspects in over 500 cases, contributing to solving crimes ranging from theft to violent assaults.
Washington County, Oregon.The Sheriff's Office reported that its facial recognition system was used to identify suspects in over 300 cases, aiding in the resolution of crimes including fraud, theft, and drug-related offenses.
Benefits of Police Use of Face Recognition

The employment of facial recognition technology by police departments has been the subject of significant discussion. Despite worries about privacy and civil liberties, there are some possible benefits to its usage in law enforcement. Here are some of the main advantages.
Enhanced Public Safety and Crime Prevention
Facial recognition can quickly match suspects with existing databases, helping police identify and apprehend criminals more efficiently. This is particularly useful in cases where time is critical, such as during active shooter situations or terror attacks.
Increased Efficiency in Investigations
Traditional methods of identifying suspects, such as manual searches through photographs, are time-consuming. Facial recognition can automate this process, allowing officers to allocate their time to other critical tasks. Plus, by re-analyzing evidence from cold cases with facial recognition, police can potentially find matches that were previously missed, leading to new leads and resolutions in long-unsolved crimes.
By automating the identification process, police departments can better allocate their resources, focusing human effort where it is most needed rather than on routine identification tasks.
Improved Accuracy in Suspect Identification
Advances in facial recognition technology have led to improved accuracy in identifying individuals, reducing the chances of mistaken identity compared to older identification methods like eyewitness testimony, which can be unreliable.
Deterrent Effect
The knowledge that facial recognition technology is in use can act as a deterrent for potential criminals, who may be less likely to commit crimes if they know there is a higher chance of being identified and caught.
Support for Counter-Terrorism Efforts
Facial recognition can be crucial in identifying individuals on watch lists or those involved in terrorist activities, both in real-time at public events and through post-event investigations.
Enhancing border security by matching faces at checkpoints against databases of known terrorists or criminals can prevent the entry of dangerous individuals into the country.
Augmentation of Existing Surveillance Systems
Facial recognition can be integrated with existing CCTV networks to automatically scan for and identify individuals involved in criminal activities, enhancing the effectiveness of public surveillance systems.
Concerns and Criticisms of Police Use of Face Recognition
The use of facial recognition technology by police has sparked significant concerns and criticisms. Here are the key issues associated with its implementation in law enforcement:
Privacy Invasion
Facial recognition allows for widespread surveillance, potentially leading to a society in which citizens are continually monitored. This raises serious privacy concerns and could have a chilling effect on free speech and assembly. The collecting, storage, and possible sharing of biometric data can be invasive. This sensitive information is at danger of being misused or accessed without authorization.
Accuracy and Bias Issues
Facial recognition systems are not infallible. They can produce false positives (misidentifying innocent people as suspects) and false negatives (failing to identify actual suspects), which can lead to wrongful arrests and undermine public trust in law enforcement.
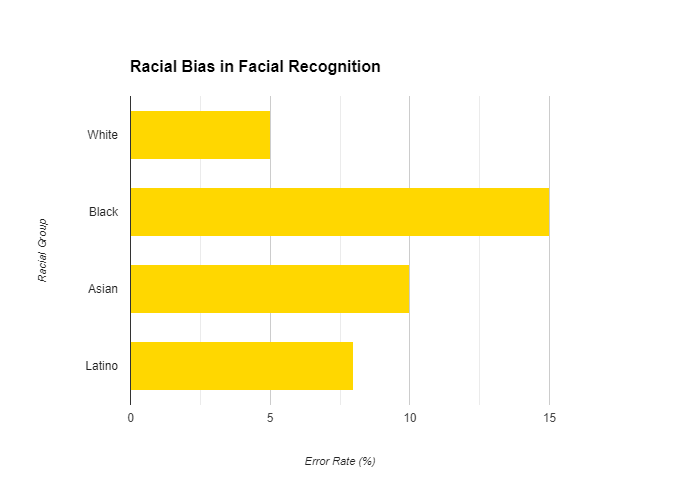
Studies have shown that facial recognition technology often has higher error rates for women and people of color. This can exacerbate existing biases in policing and lead to disproportionate targeting of minority communities.
Impact on Civil Liberties
The pervasive use of facial recognition can deter people from participating in public protests or other activities where they might be surveilled, undermining their constitutional rights.
There is a risk that reliance on facial recognition technology might lead to shortcuts in the legal process, with less emphasis on corroborating evidence and more on potentially flawed technological matches.
Lack of Transparency and Accountability
Often, the deployment and operational details of facial recognition by police are not transparent to the public. This lack of transparency can erode public trust and make it difficult to hold authorities accountable.
Ensuring proper oversight of the technology's use is challenging. Without rigorous checks and balances, there is potential for misuse and abuse by law enforcement.
Security Risks
The storage of facial recognition data is vulnerable to hacking and unauthorized access. Data breaches can expose sensitive biometric information, leading to identity theft and other security issues. There is also a risk that facial recognition technology could be misused for purposes beyond its intended scope, such as tracking political activists or targeting individuals for non-criminal reasons.
Ethical Concerns
The use of facial recognition by police can undermine community trust, especially if perceived as a tool for mass surveillance rather than targeted, lawful policing. Additionally, many people are unaware that their biometric data is being collected and processed, raising ethical concerns about consent and autonomy. These issues highlight the need for transparency and clear regulations to ensure that facial recognition technology is used responsibly and ethically.
The Future of Police Use of Face Recognition

The future of police use of facial recognition technology is likely to be shaped by a combination of technological advancements, regulatory developments, public opinion, and ethical considerations. Here are some potential directions and scenarios for its future.
Technological Advancements
Continued improvements in AI and machine learning are projected to improve the accuracy and reliability of facial recognition systems, lowering mistake rates and eliminating prejudice. This may make the technology more acceptable for use in law enforcement.
Moreover, facial recognition may be progressively coupled with other technologies, such as body-worn cameras, drones, and smart city infrastructure, enabling total surveillance capabilities.
Regulatory Developments
Growing worries about privacy and civil liberties are likely to result in stronger restrictions controlling police use of facial recognition technology. This might include explicit standards for when and how to utilize the technology, as well as transparency requirements and oversight systems.
To protect biometric data, enhanced data protection legislation may be enacted, including severe rules for data storage, access, and sharing to avoid misuse and illegal access.
Ethical Considerations
Efforts to address and mitigate biases in facial recognition algorithms will be crucial. This could involve diversifying training datasets and implementing fairness checks to ensure equitable treatment across different demographic groups.
Engaging with communities to understand their concerns and perspectives on the use of facial recognition can help shape policies that reflect public values and priorities. Community oversight boards might be established to monitor the technology’s deployment.
Public Opinion and Trust
Law enforcement agencies must endeavor to develop public trust through transparency, accountability, and prudent use of facial recognition technology. Clear communication regarding the advantages, constraints, and precautions in place will be critical.
Public education initiatives can help demystify technology and dispel myths, enabling a more informed discussion about its use and potential consequences.
Ethical and Legal Challenges
The constant challenge will be to weigh the benefits of facial recognition for public safety against the necessity to protect individual privacy and civil liberties. This equilibrium will necessitate rigorous legal and ethical considerations.
Legal challenges and court rulings will determine police officers' future use of face recognition, setting crucial precedents for acceptable usage and limitations.
Conclusion
Facial recognition technology improves police officers' capacity to identify suspects, find missing persons, and maintain public safety. To solve privacy concerns and prevent misuse, it must be used in conjunction with strong ethical standards, openness, and regulatory monitoring.
