
What Are The Differences Between KYC and AML?
While KYC and AML are integral to maintaining the integrity of financial institutions and preventing financial crimes, they serve distinct purposes and involve different processes. In this blog post, we will delve into the core differences between KYC and AML, exploring their unique roles, processes, and importance in safeguarding the financial system. This information will be helpful for financial professionals and business owners, as understanding the distinctions between KYC and AML is essential for navigating today's complex financial environment.
What is KYC?

KYC (Know Your Customer) is a crucial process by which businesses verify the identity of their customers to prevent money laundering, identity theft, financial fraud, and terrorism financing. The primary goal of KYC is to ensure that customers are who they claim to be, thereby reducing the risk of financial crimes. This verification process typically involves the use of government-issued documents, such as a driver's license or passport, to confirm both identity and address.
The KYC process serves multiple purposes, including combating money laundering, preventing terrorist financing, and curbing tax evasion. Financial institutions and businesses collect and verify customer identity documents, ensuring that the information provided is accurate and legitimate. The specific data required for verification is often determined by the policies of the exchange platform or financial institution.
There are two main approaches to verifying customer identities: manual and automated.
Manual KYC involves an in-person meeting with a company representative to verify identity through physical inspection of documents. This method, while thorough, can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Automated KYC systems, on the other hand, utilize advanced technologies to verify identities remotely, offering efficiency and scalability. Key technologies used in automated KYC include Optical Character Recognition (OCR), Machine Learning (ML), Biometric Verification.
So, in summary, KYC is a process used by businesses, particularly in the financial industry, to verify the identity of their clients. It involves collecting and assessing various forms of identification and personal information to ensure that customers are who they claim to be.
Learn more about KYC solutions here: Top KYC Services in 2024
What is AML?

Anti-Money Laundering (AML) refers to the set of laws, regulations, and procedures implemented by financial institutions and regulatory bodies to detect, prevent, and report money laundering activities. Money laundering is the process of making illegally obtained money appear legitimate, often by funneling it through various financial transactions to disguise its origins.
AML efforts are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the financial system. By implementing the measures, financial institutions help prevent the funding of illegal activities, such as terrorism, drug trafficking, and corruption. Moreover, robust AML practices protect the institutions themselves from legal and reputational risks associated with being involved, knowingly or unknowingly, in money laundering schemes.
Governments and international organizations play a key role in setting AML standards and regulations. Agencies such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) develop global policies to combat money laundering and promote the effective implementation of legal, regulatory, and operational measures. Compliance with AML regulations is not just a legal obligation but also a critical component of global financial security and stability.
AML regulations require financial institutions to:
Maintain records. Keep detailed records of transactions to create an audit trail.
Report specific transactions. Disclose certain transactions to government agencies, especially those that appear suspicious.
Conduct due diligence. Perform thorough checks on customers to verify their identities and assess the risk they pose.
In summary, Anti-Money Laundering (AML) encompasses a comprehensive framework aimed at identifying, preventing, and reporting money laundering activities. Through diligent monitoring, reporting, and compliance, financial institutions contribute to a safer and more transparent financial system.
Learn more here about AML solutions: Top AML Solutions in 2024
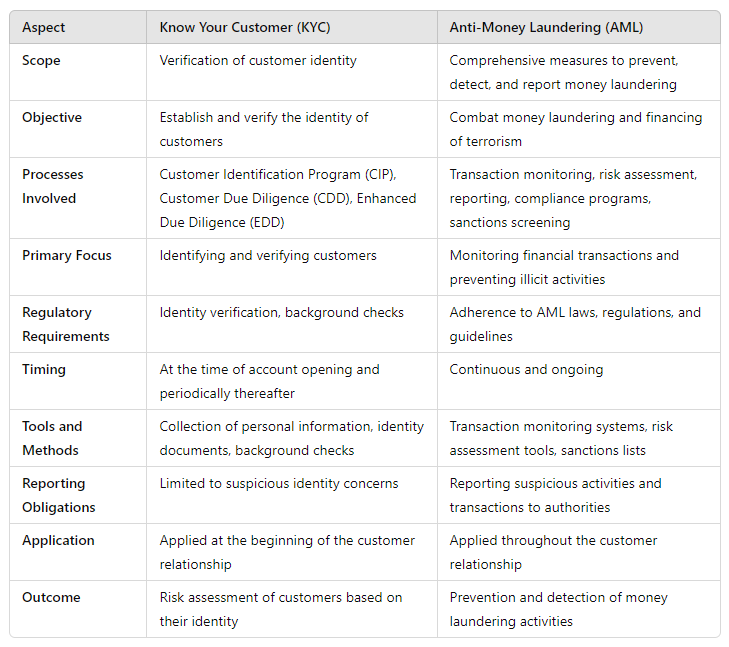
Differences between KYC and AML
KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) are two fundamental components in the realm of financial security and regulatory compliance. While they are often mentioned together and overlap in their objectives of preventing financial crimes, they are distinct in their focus, processes, and regulatory frameworks. Understanding the differences between KYC and AML is crucial for any organization involved in financial transactions and services.
Purpose and Focus
The overarching aim of KYC procedures is to authenticate the identities of customers and evaluate the potential risks they may bring before granting them account access or transaction privileges. KYC emphasizes thorough customer identification and diligent scrutiny, enabling financial institutions to understand their clientele, their financial behaviors, and the associated risk levels.
AML initiatives, on the other hand, are geared towards thwarting and uncovering money laundering endeavors and other illicit financial activities, such as funding terrorism. AML efforts encompass a broader spectrum of activities, spanning from identifying and reporting suspicious transactions to monitoring financial activities and maintaining meticulous records to trace unlawful behavior.
Processes and Procedures
When discussing processes and procedures, KYC involves:
Customer identification. Verifying the identity of the customer using official documents like passports, driver's licenses, and utility bills.
Customer Due Diligence (CDD). Conducting background checks to understand the customer’s financial behavior and assess their risk level.
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD). Applying additional scrutiny to high-risk customers to ensure thorough verification and risk assessment.
Speaking about AML, it involves:
Transaction monitoring. Continuously monitoring customer transactions to identify unusual or suspicious patterns that could indicate money laundering.
Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR). Filing reports to relevant authorities when suspicious activities are detected.
Risk assessment and management. Evaluating and managing the risks associated with different customers, transactions, and geographic locations.
Regulatory Frameworks
KYC regulations vary by country but generally include guidelines for verifying customer identities and performing due diligence. Financial institutions must comply with these regulations to prevent fraud and identity theft. Organizations like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) provide international standards and recommendations for KYC practices.
AML regulations are more comprehensive. They include measures for monitoring and reporting suspicious activities, maintaining records, and conducting regular audits. These regulations are designed to prevent and detect money laundering and related crimes. FATF, along with other organizations like the European Union’s AMLD (Anti-Money Laundering Directives), provides detailed guidelines and best practices for AML compliance.
Impact on Financial Institutions
KYC processes are critical during the customer onboarding phase, ensuring that only legitimate customers are granted access to financial services. Effective KYC helps mitigate risks associated with fraud, identity theft, and financial crime by verifying customer identities and assessing their risk profiles.
Similarly, AML involves continuous monitoring of customer activities and transactions to detect and prevent money laundering. Financial institutions must adhere to AML regulations to avoid severe penalties, fines, and reputational damage. AML compliance is a continuous process that requires ongoing effort and resources.
In summary, KYC is primarily concerned with confirming the identity of clients during account initiation and on a recurring basis. Conversely, AML encompasses a wide range of strategies to thwart, identify, and disclose instances of money laundering.
The objective of KYC is to validate customer identities, reducing the likelihood of illicit financial activities. Meanwhile, AML endeavors to counteract money laundering and terrorism financing through vigilant transaction oversight and adherence to regulatory standards.
KYC procedures entail identity authentication and diligent examination of client information. In contrast, AML involves continuous transaction monitoring, risk evaluation, reporting mechanisms, and adherence to global sanctions.
Why Both KYC and AML are Essential

In the complex and ever-evolving world of finance, ensuring the integrity and security of financial systems is paramount. That’s why KYC and AML are critical components of a robust financial security framework, but they serve distinct purposes that complement each other in protecting financial institutions and the broader economy.
Preventing Financial Crimes
One of the primary reasons both KYC and AML are essential is their role in preventing financial crimes. KYC processes involve verifying the identity of customers and assessing their risk levels. By ensuring that institutions know who they are dealing with, they can better identify suspicious activities from the outset. On the other hand, AML measures focus on monitoring transactions and identifying patterns that may indicate money laundering or other illicit activities. Together, KYC and AML create a comprehensive defense mechanism against various forms of financial crime, including fraud, money laundering, and terrorist financing.
Protecting Financial Institutions
Financial institutions are at the forefront of combating financial crimes. KYC and AML practices are vital in shielding these institutions from being exploited by criminals. KYC helps banks and other financial entities to establish the legitimacy of their clients, thereby reducing the risk of onboarding fraudulent individuals or entities. AML, meanwhile, involves ongoing monitoring of transactions and activities, ensuring that any suspicious behavior is detected and addressed promptly. This not only protects the institutions from potential losses but also helps maintain their reputation and trust among customers and regulators.
Ensuring Compliance
Compliance with regulatory requirements is another crucial aspect that underscores the importance of KYC and AML. Financial regulators around the world have established stringent guidelines to combat financial crimes. KYC and AML procedures are at the heart of these regulations. By implementing robust KYC and AML protocols, financial institutions ensure they are in compliance with local and international laws. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, including hefty fines and loss of operating licenses. Therefore, adherence to KYC and AML regulations is not just about mitigating risks but also about maintaining operational legitimacy and avoiding legal repercussions.
Enhancing Customer Trust
Effective KYC and AML processes reassure customers that their financial institutions are diligent about safeguarding their assets and personal information. When customers see that their bank is proactive in preventing fraud and money laundering, their confidence in the institution's reliability and integrity is strengthened. This trust is crucial for customer retention and overall business success.
Supporting Global Financial Stability
The interconnectedness of the global financial system means that the impact of financial crimes can be far-reaching. Money laundering and terrorist financing, for instance, have global ramifications. KYC and AML practices help maintain the stability and integrity of the global financial system by preventing illicit funds from flowing through it. This contributes to economic stability and security worldwide, making it harder for criminal organizations to finance their activities.
In conclusion, KYC and AML are not merely regulatory requirements; they are fundamental to the health and security of financial systems. By preventing financial crimes, protecting institutions, ensuring compliance, enhancing customer trust, and supporting global financial stability, these practices are indispensable in today's financial landscape. Financial institutions must continue to invest in and prioritize robust KYC and AML frameworks to safeguard their operations and contribute to a safer global economy.
Luxand.cloud KYC Solution
Luxand.cloud offers an advanced KYC solution that addresses the needs of financial institutions, fintech companies, and other organizations requiring robust identity verification processes. Leveraging face recognition technology, Luxand.cloud provides a seamless and secure KYC experience, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements while enhancing customer trust and operational efficiency.

Advanced Facial Recognition Technology
At the core of Luxand.cloud's KYC solution is its state-of-the-art facial recognition technology. This technology ensures accurate and swift identity verification by comparing a customer's live image or video with their official identification documents. The advanced algorithms used in facial recognition can detect and prevent fraud attempts, such as spoofing attacks, making the KYC process highly secure. This technology not only enhances security but also speeds up the verification process, providing a better customer experience.
Real-Time Identity Verification
One of the standout features of Luxand.cloud's KYC solution is its ability to perform real-time identity verification. This means that customers can be verified almost instantly, reducing the time it takes to onboard new clients. Real-time verification is crucial for businesses that need to quickly approve new accounts without compromising on security. By streamlining the KYC process, Luxand.cloud helps organizations improve their operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Enhanced User Experience
Luxand.cloud places a strong emphasis on user experience. The KYC solution is designed to be user-friendly, with an intuitive interface that guides customers through the verification process step-by-step. This ease of use reduces the likelihood of errors and improves the overall customer experience. Additionally, the solution can be easily integrated into existing systems and workflows, ensuring a seamless implementation for businesses.
Scalability and Flexibility
The Luxand.cloud KYC solution is highly scalable, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large multinational corporations. It can handle a high volume of verification requests without compromising on performance or accuracy. Additionally, the solution is flexible, allowing organizations to customize the verification process to meet their specific needs and regulatory requirements.
Data Security and Privacy
Our KYC solution employs robust encryption methods to protect customer data during transmission and storage. It also adheres to strict data privacy regulations, ensuring that customer information is handled with the highest level of confidentiality and integrity.
Conclusion
In summary, while KYC and AML are both integral to maintaining financial security and regulatory compliance, they serve different yet complementary purposes. KYC is primarily concerned with verifying customer identities and assessing risks at the initial stages of the customer relationship. AML, on the other hand, focuses on monitoring, detecting, and reporting suspicious activities to prevent money laundering and other financial crimes. Both KYC and AML are essential for protecting financial institutions and the broader financial system from abuse and ensuring adherence to regulatory standards.
